Start here: how our SEO split tests work
If you aren't familiar with the fundamentals of how we run controlled SEO experiments that form the basis of all our case studies, then you might find it useful to start by reading the explanation at the end of this article before digesting the details of the case study below. If you'd like to get a new case study by email every two weeks, just enter your email address here.
This week’s #SPQuiz, we asked our followers whether they thought we could improve organic traffic by implementing article schema on article pages.
Here is what they thought:
Twitter:
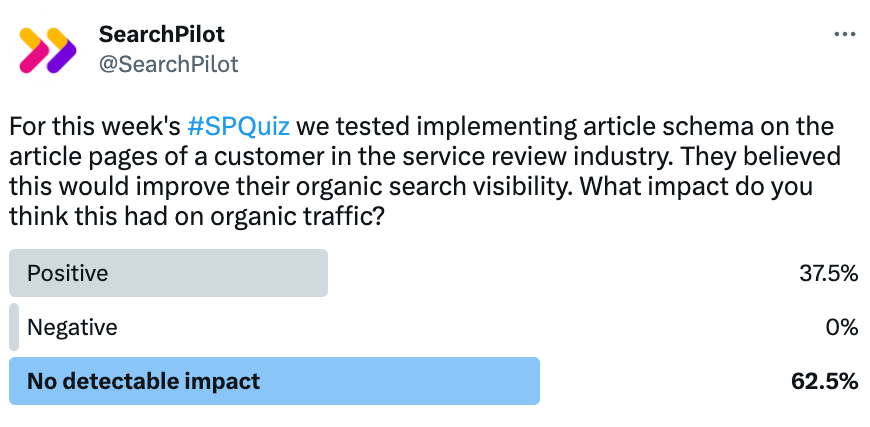
About 60% of you believed that adding article schema to article pages had no detectable impact on organic traffic, while 38% think there was a positive impact.
LinkedIn:
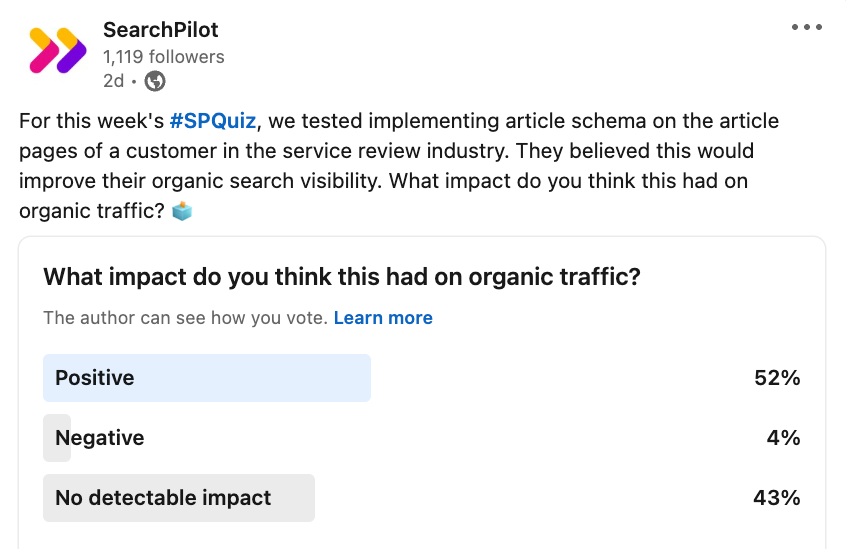
On LinkedIn, our followers believed slightly differently, with 52% believing that adding article schema had a positive impact and 43% saying there was no detectable impact to organic traffic.
So, which one was it? Read the full case study below to find out!
The Case Study
Article schema is a widely recognized form of structured data markup designed to assist search engine crawlers in comprehending structured information about articles and blog posts. Although including essential details like titles, authors, and publication dates aims to be beneficial to SEO, the true impact on organic traffic and click-through rates remains to be determined.
In light of this, a customer in the service review industry recently implemented article schema on their article pages. By adopting this approach, they aimed to enhance their search engine visibility, provide users with more informative content, and ultimately elevate the overall customer experience.
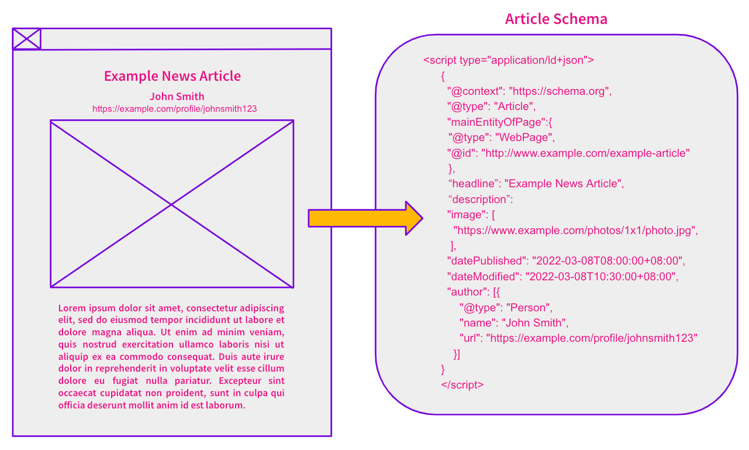
To simplify the process of creating dynamic variables and incorporating the article schema, we utilized the capabilities of the SearchPilot platform to create these values and then refined it using regular expression. This enabled us to seamlessly define and integrate the necessary schema attributes within the HTML structure at scale.
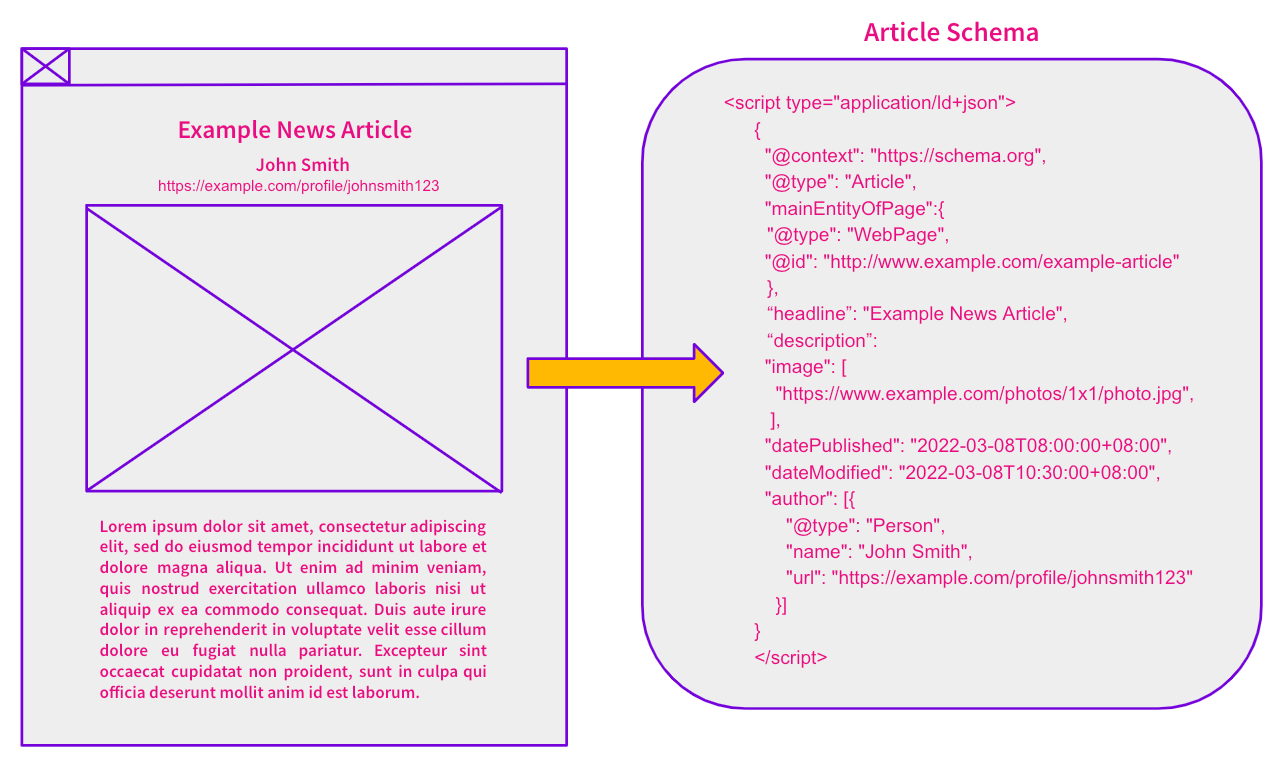
Below is an example of how the schema was setup:
The chart below shows the impact of this test on organic sessions:
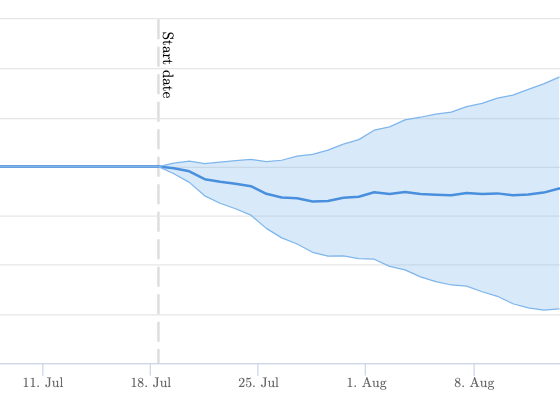
We didn’t see a clear negative impact on organic traffic when we added article schema to our pages. However, Google has confirmed that they use article-structured data to better understand the content included within article pages which, in turn, can impact the way they display the page in SERPs.
With AI becoming an ever-growing part of how search engines understand content to deliver answers to user queries, schema markup can help crawlers become more efficient in understanding the context and purpose of pages. While the direct impact of this is harder to measure, it’s an important factor to consider when deciding whether or not to implement article schema.
In keeping with our “default to deploy” mindset, even though the test was inconclusive, we decided to implement the change, as we believe that even small benefits are worth exploring and no negative impact was seen.
How our SEO split tests work
The most important thing to know is that our case studies are based on controlled experiments with control and variant pages:
- By detecting changes in performance of the variant pages compared to the control, we know that the measured effect was not caused by seasonality, sitewide changes, Google algorithm updates, competitor changes, or any other external impact.
- The statistical analysis compares the actual outcome to a forecast, and comes with a confidence interval so we know how certain we are the effect is real.
- We measure the impact on organic traffic in order to capture changes to rankings and/or changes to clickthrough rate (more here).
Read more about how SEO testing works or get a demo of the SearchPilot platform.